Business cases and application scenarios
Business cases
Content Distributor (purchased signal)
A network operator has the possibility to purchase a TV and a DOCSIS signal from a provider or another operator (i.e. the entire broadband spectrum). The delivery is coaxial or via (analog) fibre optics. AXING products are used to distribute the signals in the network up to the antenna outlet.
Content Provider (generate signal completely or partially by yourself)
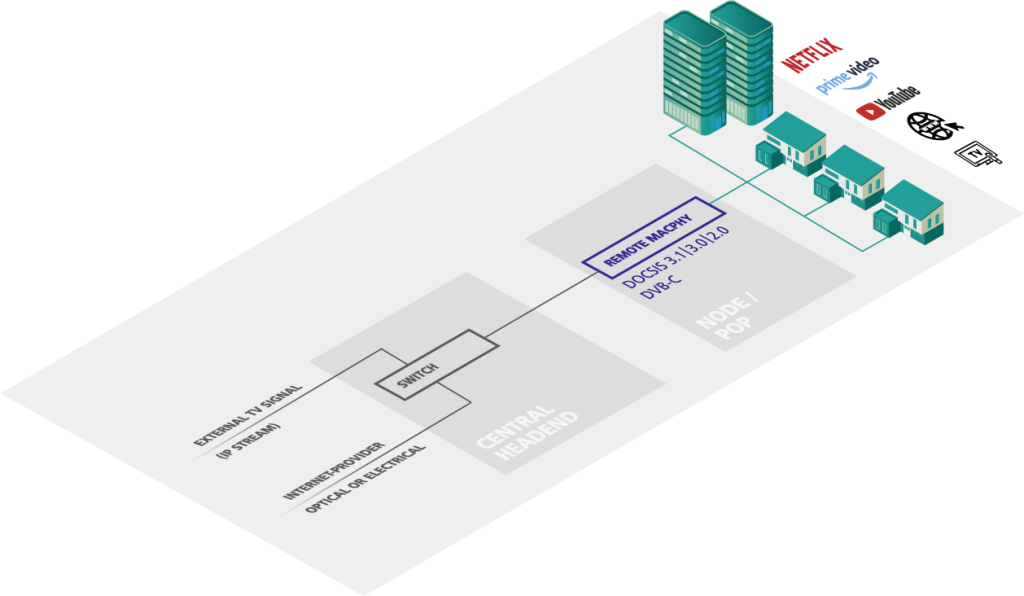
TV signal purchased, Internet signal self-generated
A network operator has the option of purchasing a TV signal from a provider and generating the broadband Internet DOCSIS signal to the consumer itself. The TV signal is delivered via IP, an EdgeQAM converts the IP signal into DVB-C channels. The DOCSIS signal is generated by DEV-Remote-MACPHY and connected to the broadband network via a 10G connection. AXING articles are used for the distribution of the signals in the network up to the wall socket.
TV signal self-generated, Internet signal purchased
A network operator can generate a TV signal itself. AXING headend technology is used for this. The DOCSIS signal is delivered coaxially or via (analogue) fibre optics. AXING products are used to distribute the signals in the network up to the antenna socket.
TV and Internet signal self-generated – maximum added value for the operator
A network operator can generate the entire broadband cable spectrum itself. AXING headend technology is used for TV signal generation. The DOCSIS signal is generated via a 10G connection to the broadband network using DEV-Remote-MACPHY. AXING products are used to distribute the signals in the network up to the wall socket.
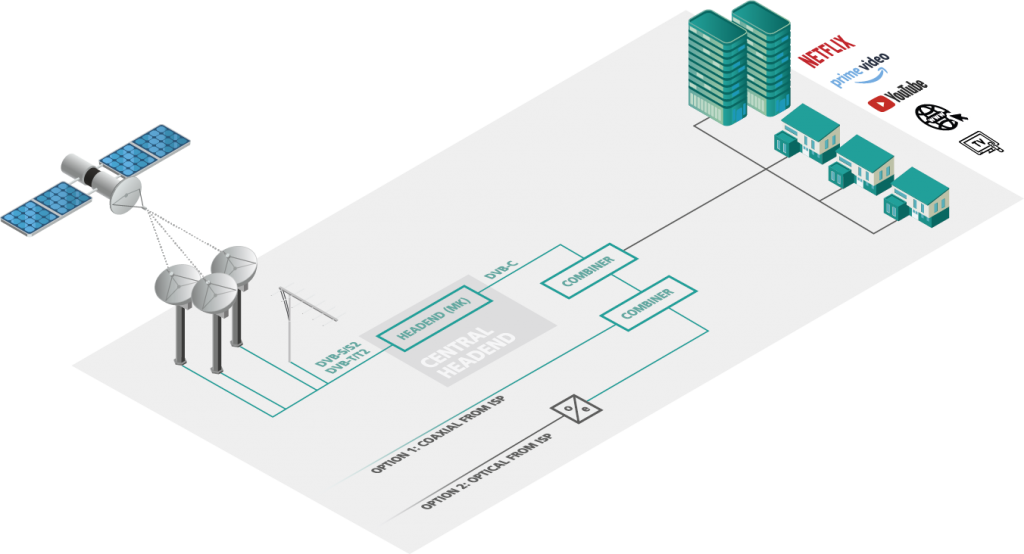
Reselling the signal
A network operator can resell the signals generated by itself. The transmission to a customer can be coaxial or via analogue optical fibre. However, TV bouquets can also be provided as IP streams.
Interoperability with GPON and other digital FTTH systems
If a digital optical signal is used to provide households with fast Internet access, it is still possible to transmit TV (or DOCSIS signals) using wavelength division multiplexing over the same fibre. In this way, TV supply can be guaranteed with classic AXING headend technology.
Szenarios
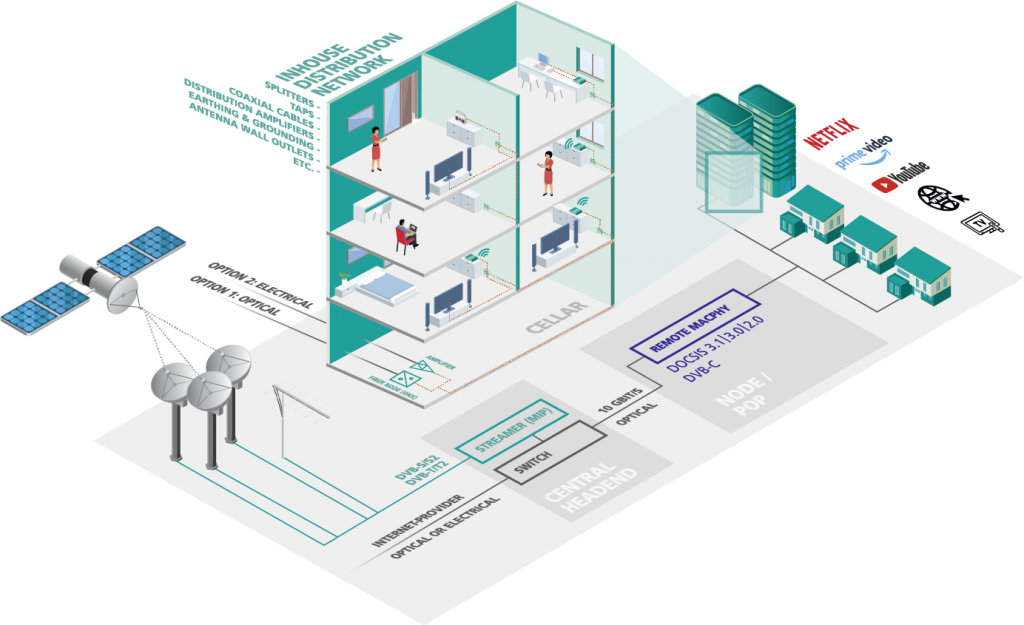
Inhouse Distribution
The feed to the buildings is either coaxial or analogue-optical (FTTH, FTTB) with DVB-C for television and DOCSIS for Internet and telephony. When fed optically via a fibre node from AXING, the signal is converted for the coaxial cable inside the building. In the case of coaxial feed, the signal is amplified. For further distribution in the house, use AXING products – from amplifiers, distributors and splitters to multimedia sockets with TV and DATA ports.
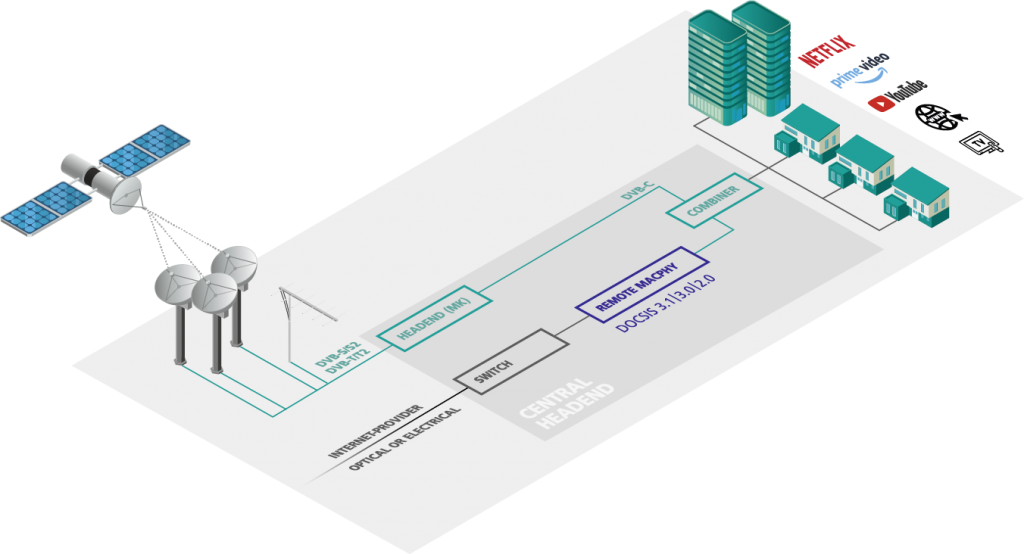
Own DVB-C headend for coaxial network
Generate TV signals yourself and feed them into the coaxial cable network as DVB-C channels. You can obtain the Internet signal from a provider with electrical or optical feed. A DOCSIS signal is generated via the connected remote CCAP node. DVB-C and DOCSIS signals are combined and fed in.
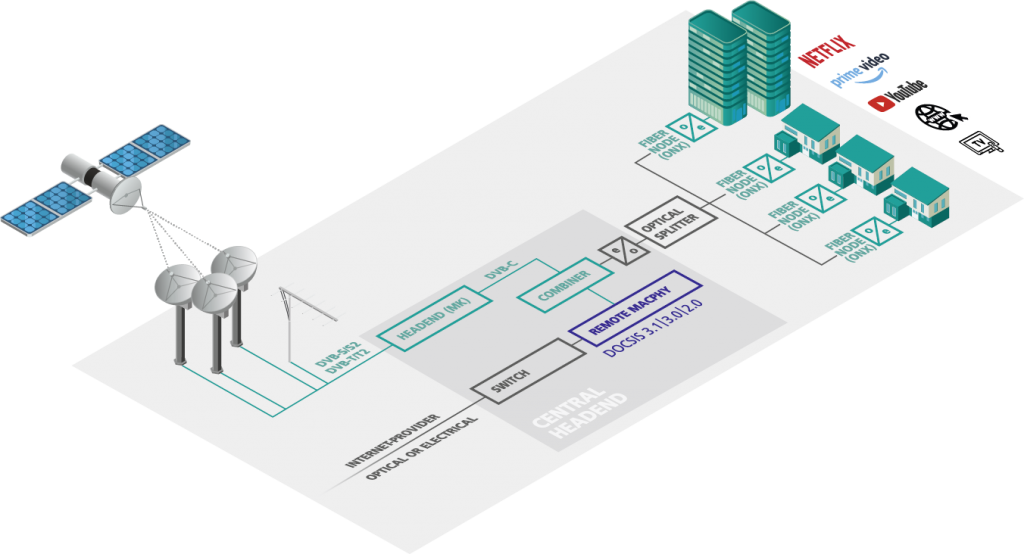
Own DVB-C headend for fibre optical network
Generate TV signals yourself and feed them as DVB-C channels into an optical FTTB fibre optic network. You can obtain the Internet signal from a provider with electrical or optical feed. A DOCSIS signal is generated via the connected remote CCAP node. DVB-C and DOCSIS are combined and fed in optically. Via AXING fibre nodes the signal is converted for the domestic coaxial cable.
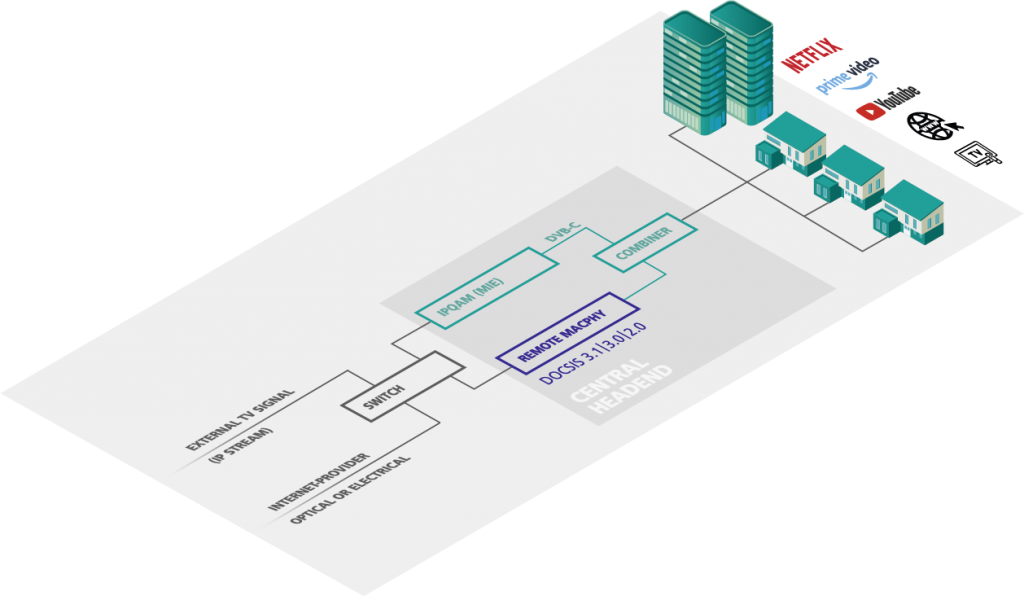
Own IPTV headend with IPQAM
Generate TV signals as IP streams in the headend and combine them via a network switch with the Internet feed for your cable network. Together, the signals are transmitted via a single cable to a node/POP. Only there is a DVB-C signal generated by an AXING IPQAM converter. A DEV Remote-CCAP converts the Internet data into DOCSIS. The signals are combined and distributed to the individual households via a combiner.
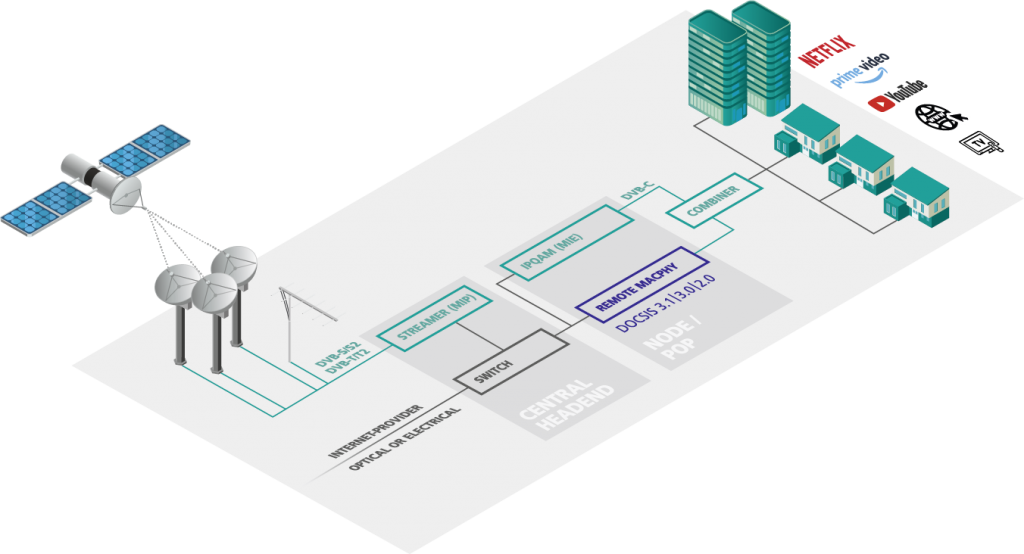
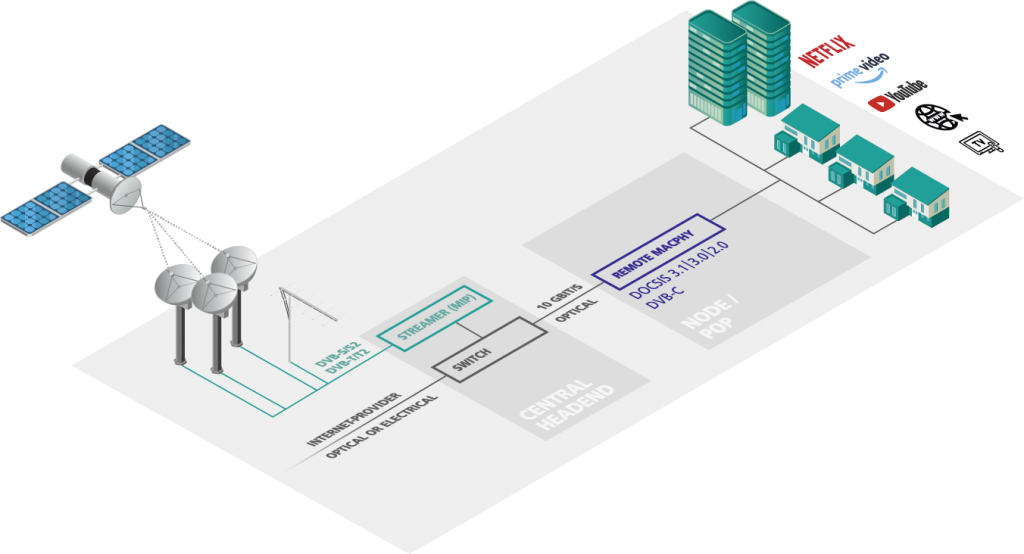
Own IPTV headend
Generate TV signals as IP streams in the headend and combine them via an (optical) network switch with the Internet feed for your cable network. Together, the signals are transmitted to a node/POP via a single cable at up to 10 Gbps. A DEV Remote-CCAP converts the IP signals into DOCSIS and DVB-C, thus generating the entire broadband cable spectrum.
TV signals generated in this way can also be sold to third parties.
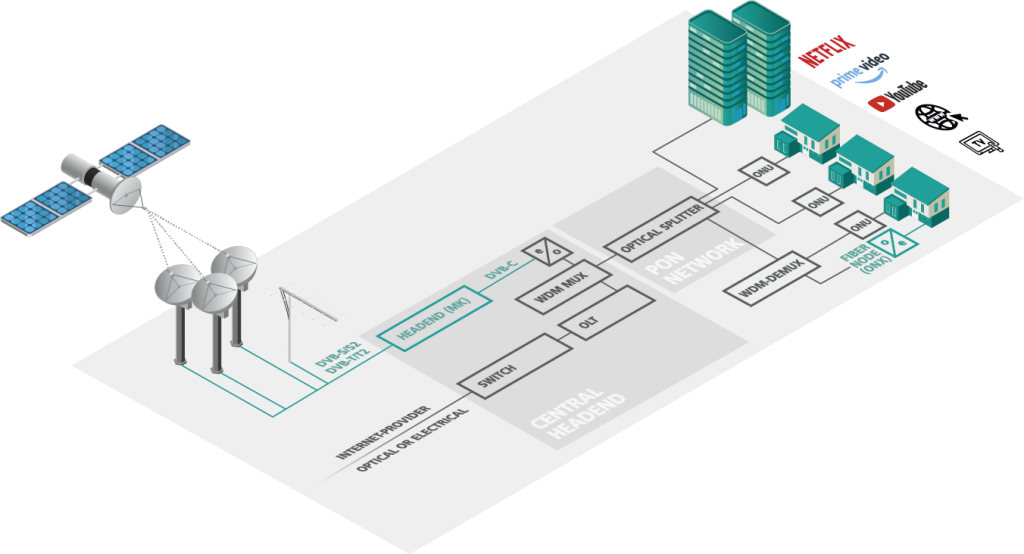
Own headend for digital fibre optical network
Generate TV signals yourself and feed them as DVB-C channels into a digital FTTB fibre optic network (e.g. GPON) using wavelength division multiplexing. Via FTTH, the connected households then receive TV and Internet from the optical termination unit ONU. Alternatively, the TV signal can also be fed into the coaxial house distribution system via an AXING fibre node.